The Filter Bar is used to apply and display filters to a data set. It is most often used with the Advanced Table, but is flexible enough to support the standard Table, lists, or a grid of cards.
Usage
When to use
- When displaying filters for a data set.
- As a replacement for the HDS Filter pattern.
When not to use
- For complex query builder features.
Type
The Filter Bar supports two visual presentations, attached and standalone, to be used in different contexts and with different types of data sets.
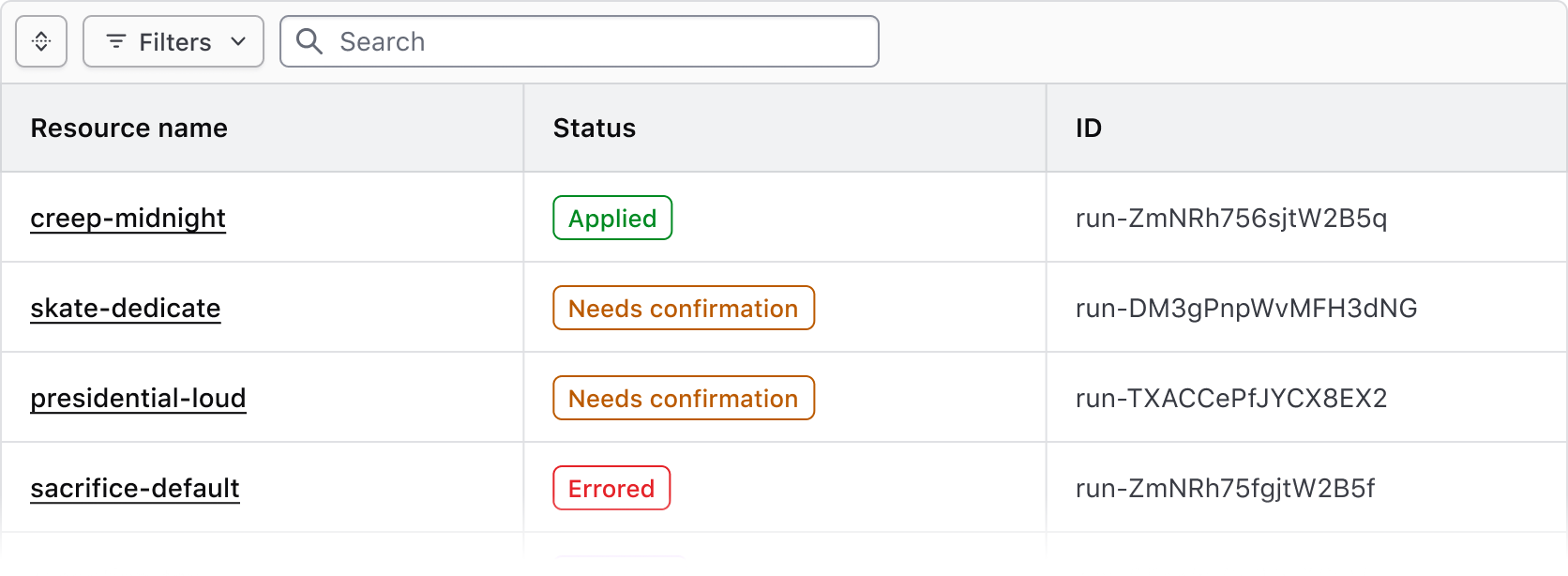
Attached
Use the attached variant with the Advanced Table to clearly associate the Filter Bar with the rendered data set and the table.
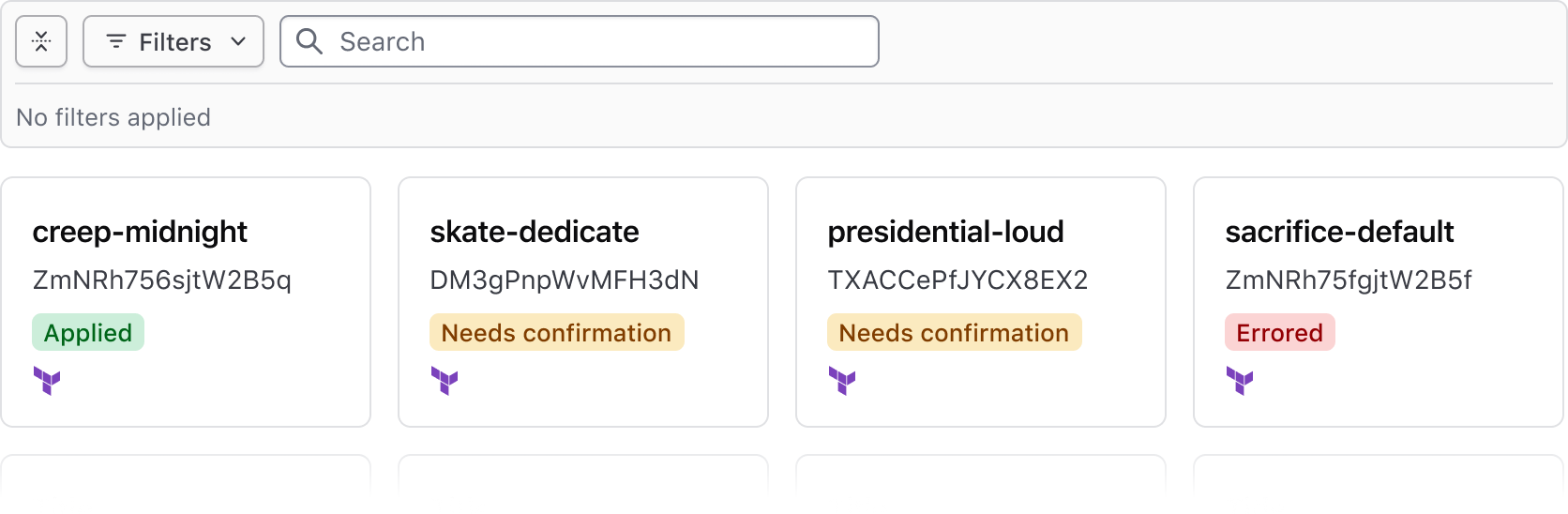
Standalone
Use the standalone variant when a data set is rendered in formats other than the Advanced Table, e.g., a standard Table, list, or grid of cards.
Applying Filters
Filters can be applied on a per-filter basis or via live filtering.
- Per-filter: filters are applied when the user confirms their selection with the "Apply filters" button in the dropdown. This is the most common method.
- Live filtering: filters are applied immediately upon selection.
Applied filters
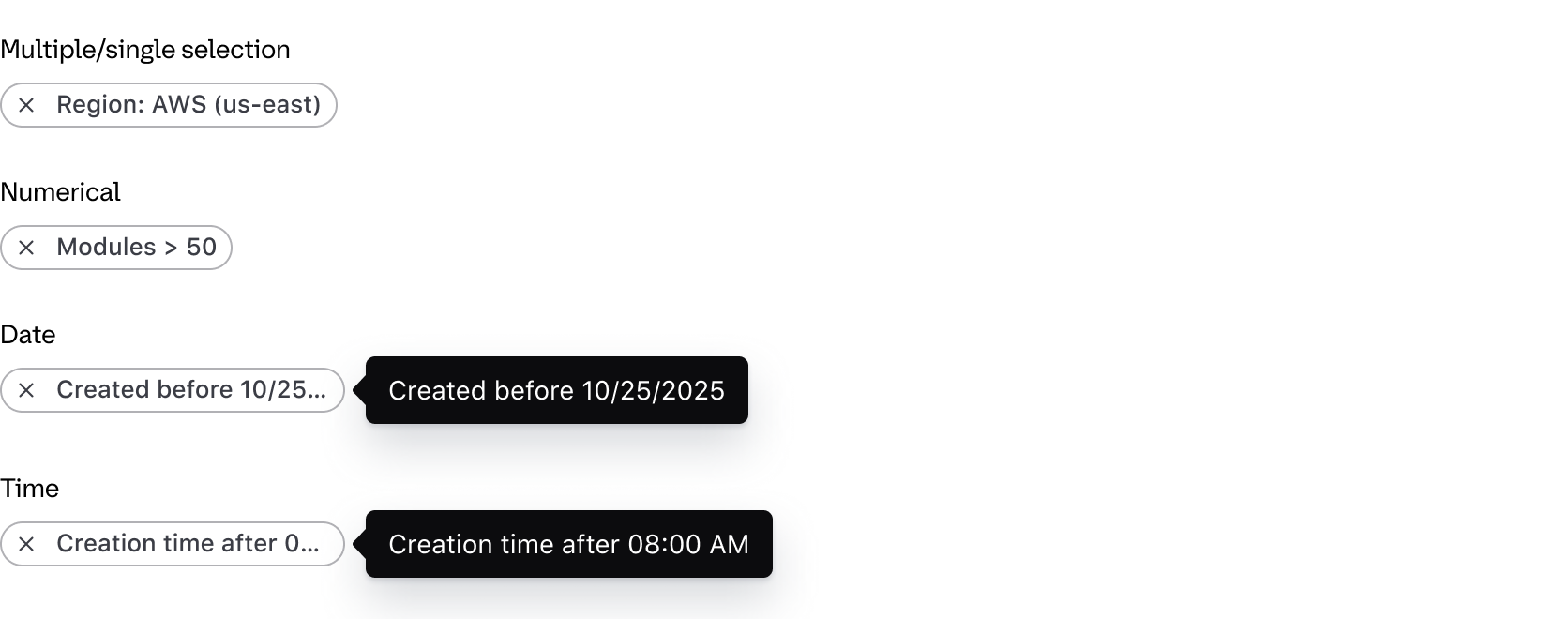
Applied filters are represented by a Tag displaying the filter parameter (the category or column the filter corresponds to) and the filter value (corresponding with the specific cell content).

By default, the text rendered within the Tag uses a standardized format depending on the type of filter:
- Single and multiple selection filters group the parameter and value using a colon, e.g., "Region: AWS (us-east)"
- Numerical filters group the parameter and value with an operator symbols, e.g., "Modules > 50"
- Date and time filters group the parameter and value with natural language, e.g., "Created before 12:00 PM"
If necessary, the text can be overridden within the Tag. This can be useful if the parameter label is an irregular plural, if the parameter reads more naturally with certain punctuation or grammar, or for product-specific reasons.
The Tag component truncates at roughly 20 characters.
Expand & collapse
The applied filters section can be collapsed to simplify the UI or expanded to bring focus to the data. This is helpful when many filters are applied or when the data set is complex.

When no filters are applied, the applied filters section is collapsed by default and will display an empty state message when expanded.

When one or more filters are applied, the Filter Bar is expanded by default.
Clearing filters
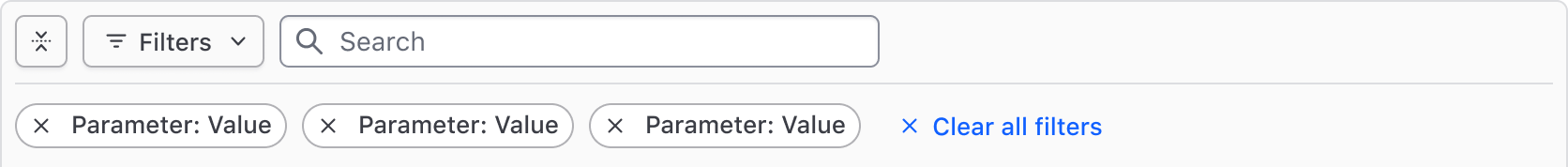
All filters can be cleared in bulk using the "Clear All" button near the applied filters or in the dropdown footer.
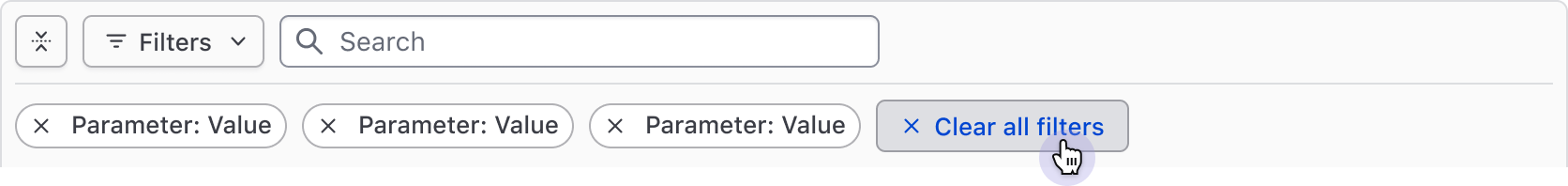
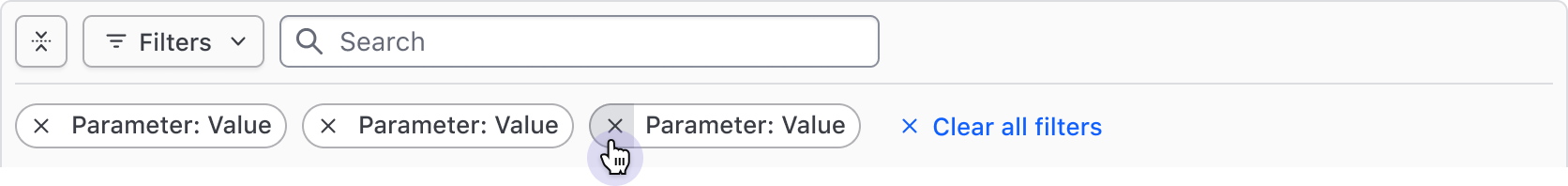
Filters can also be cleared individually via the Tag's dismiss button.
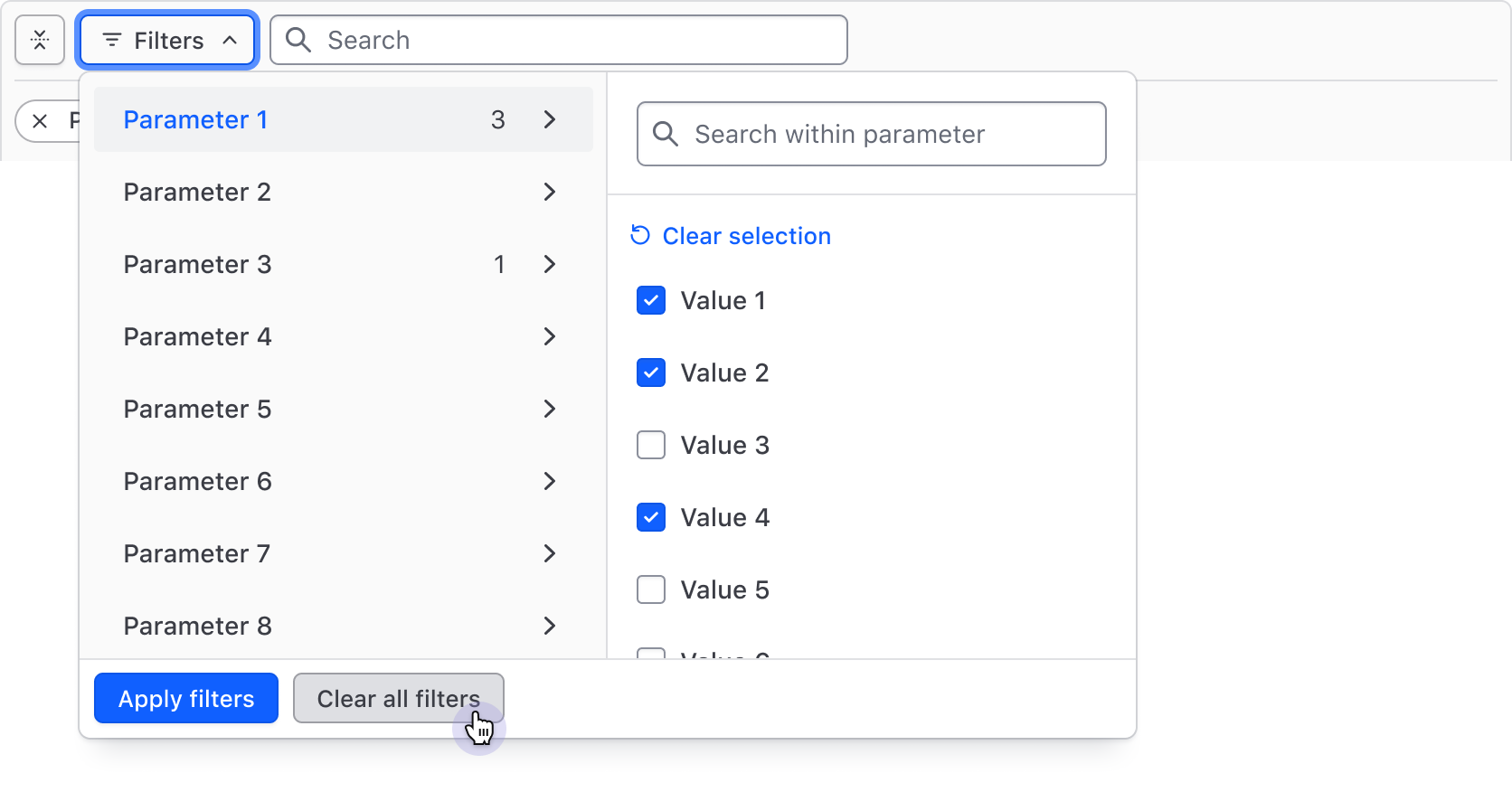
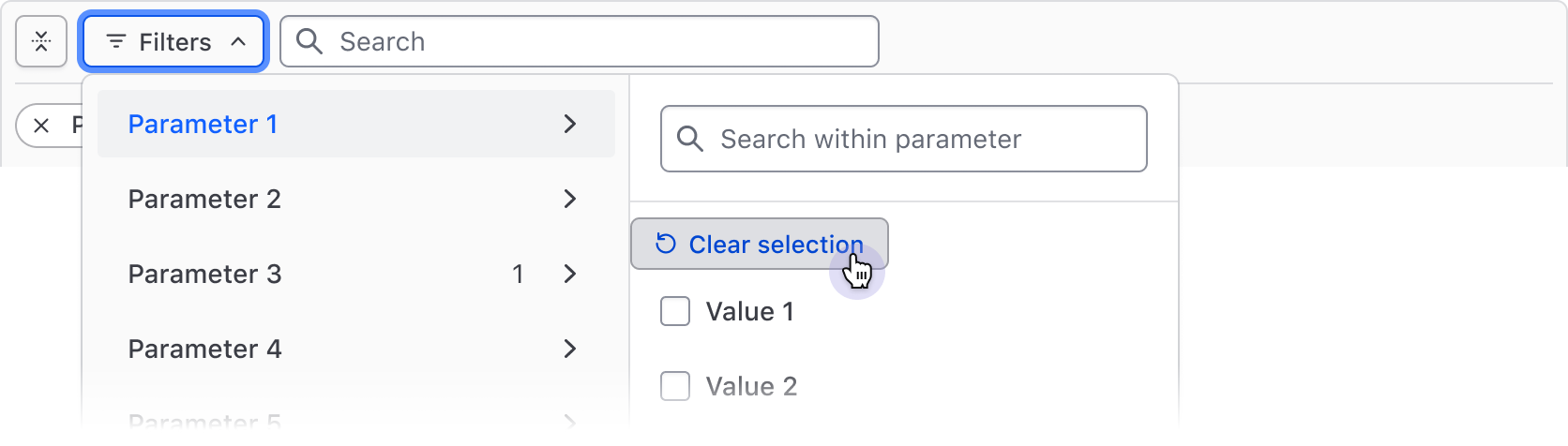
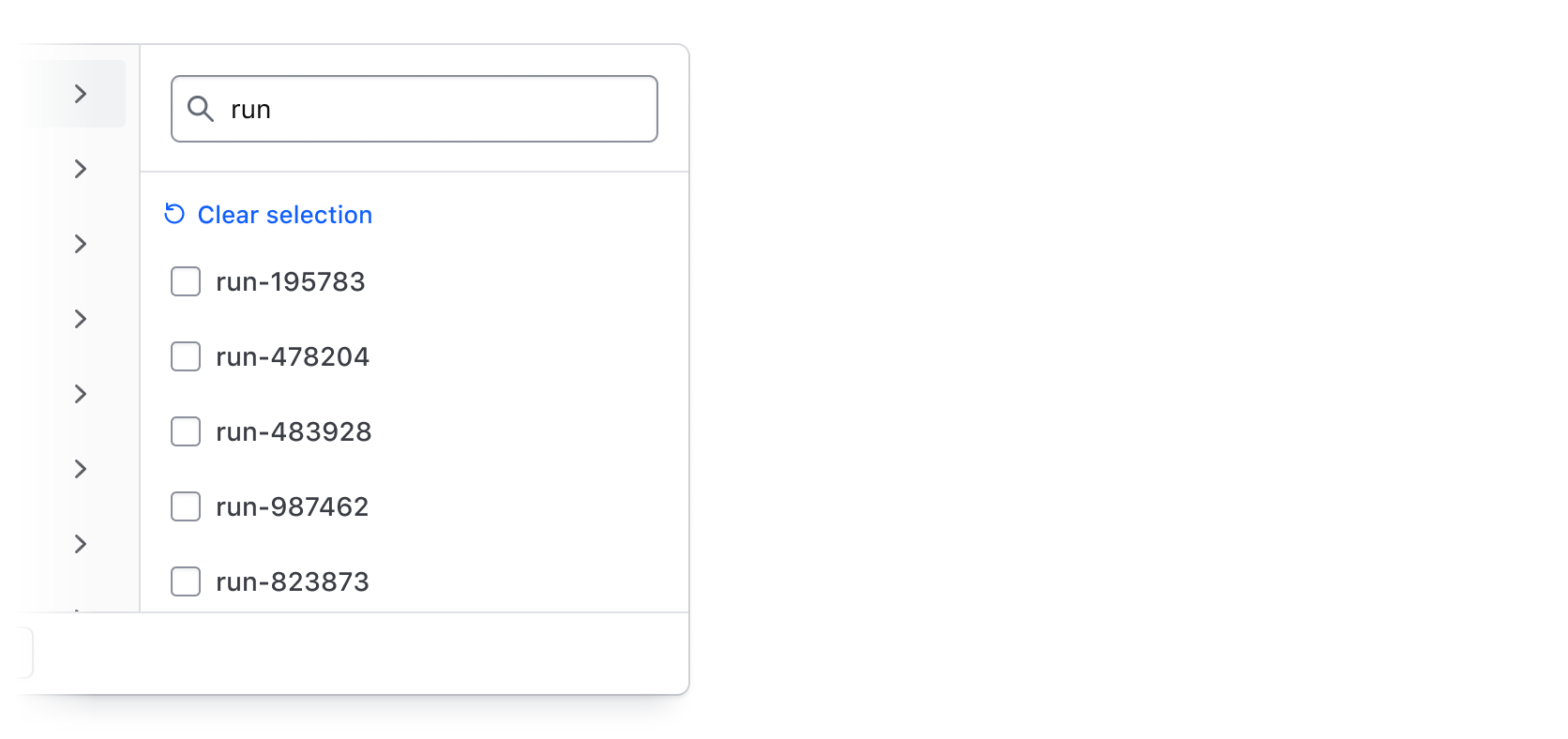
When multiple filter values are selected for a single parameter or input fields define the filter, the "Clear selection" button in the dropdown deselects all values for that parameter.
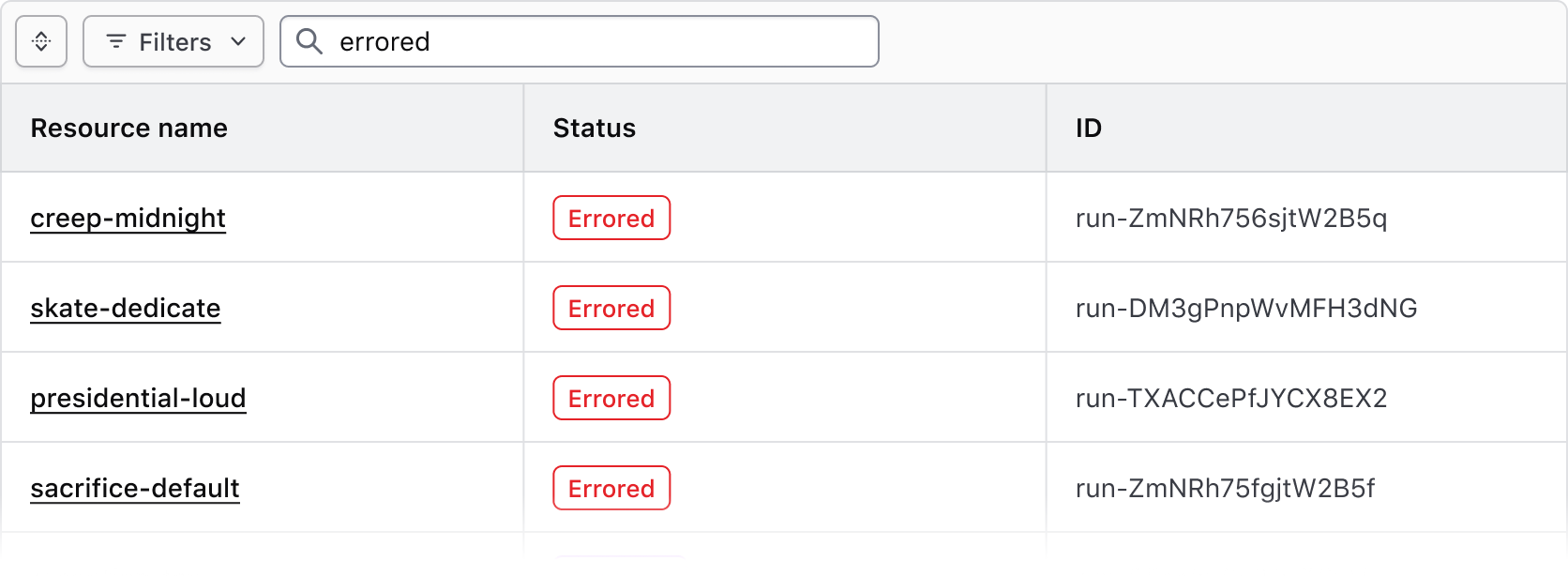
Search
Use the search input to apply a broad text filter across the entire data set.
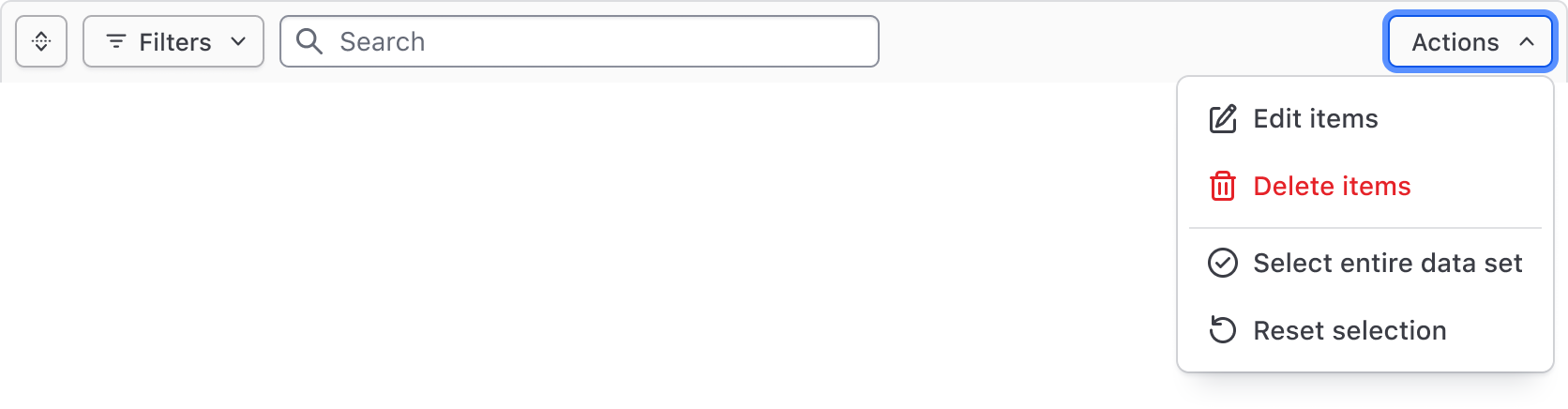
Bulk actions
Bulk actions, corresponding to our recommendations for multi-select, can be used to perform actions across multiple results, such as editing, deleting, and selecting subsets of the data set.
Generic content
Custom functionality can be added to or replace the Bulk action dropdown. We recommend limiting this to actions or information that directly tie back to the data set.
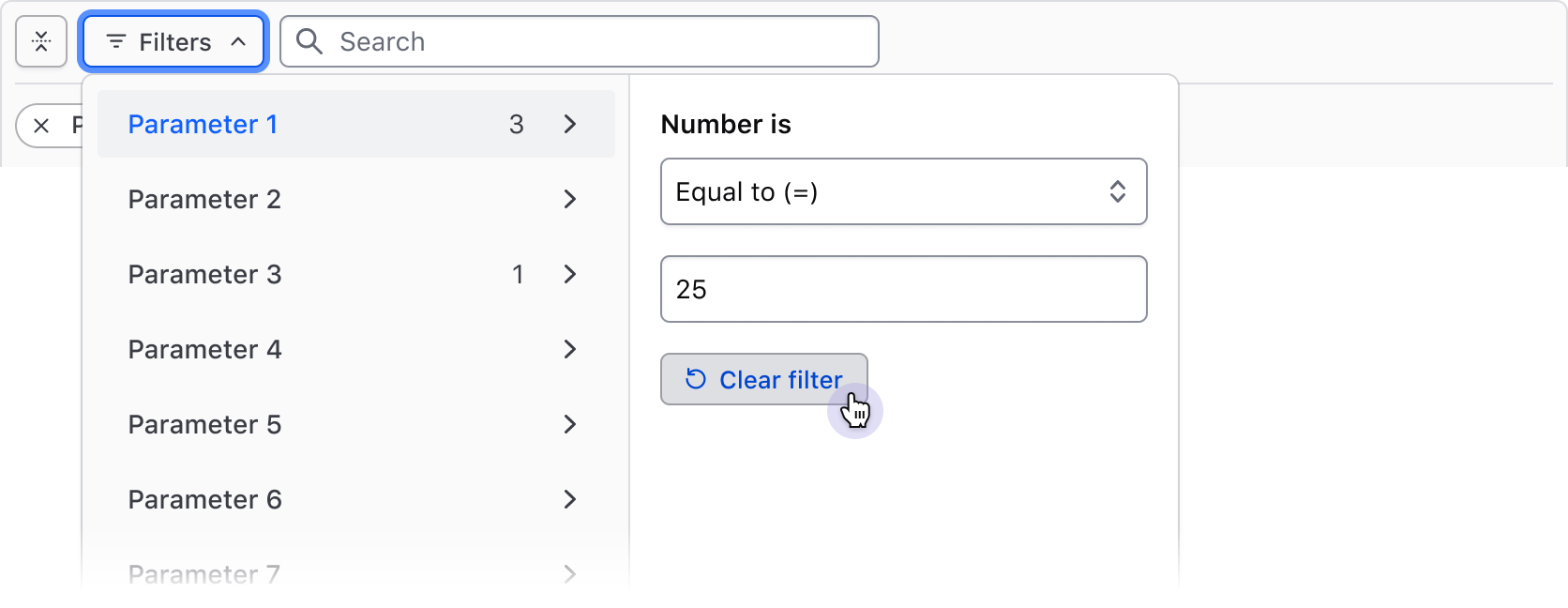
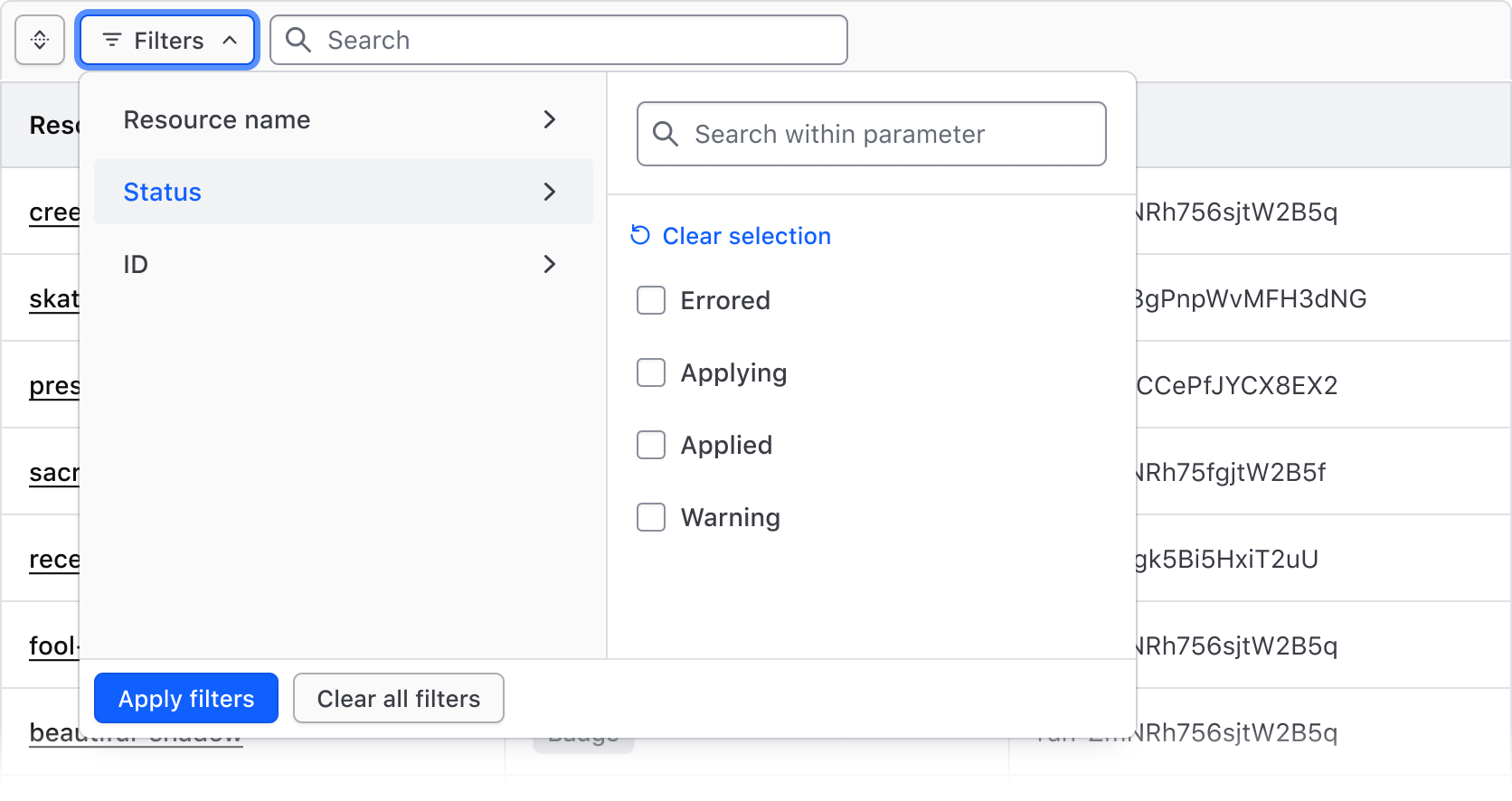
Filter dropdown
The Filter Bar includes a complex dropdown menu that displays available filter parameters, the values within each parameter, support for numerical/date/time values, value ranges, and actions to apply and clear filters.
The Filter Dropdown is responsible for the selection and application of filters and is broken into two "panels":
- The left panel displays the list of parameters (categories) that can be filtered upon.
- The right panel displays a list of options or a group of input fields (for numerical, date, or time values).
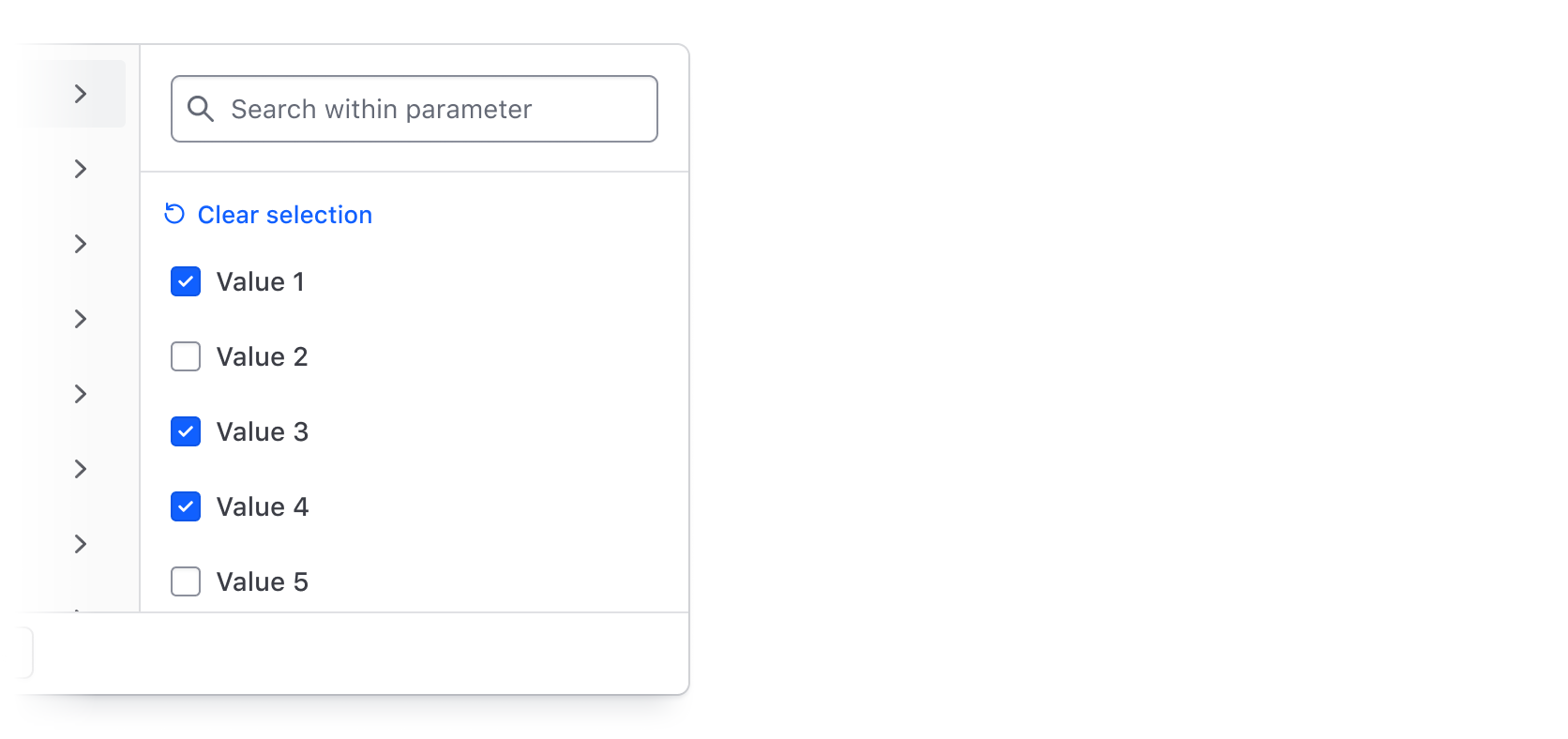
Multi-selection
Selecting multiple values from a list of options is one of the most common filtering methods. It's best suited for categorical data like statuses, but can also be used more generally to filter by a handful of text or string values.
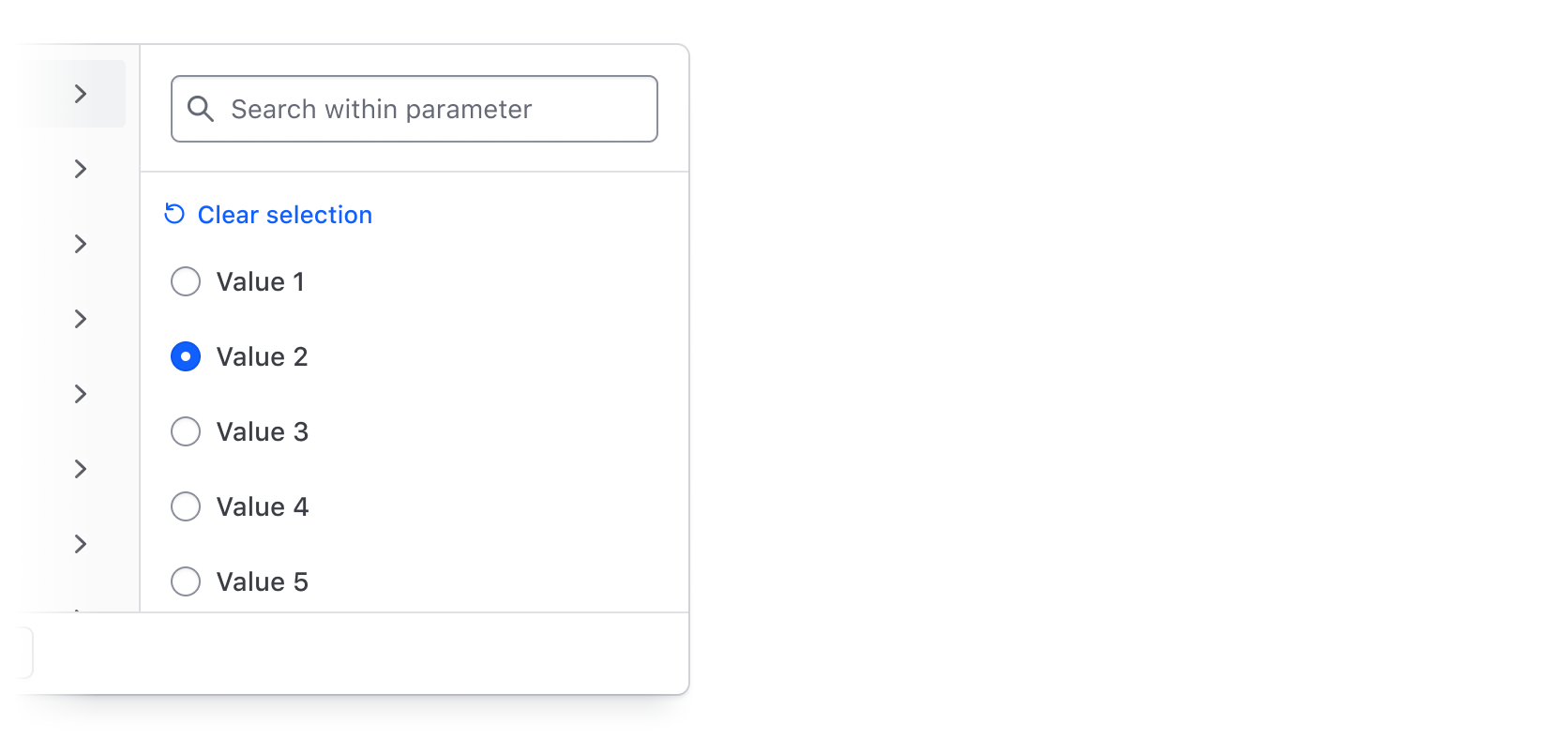
Single-selection
Selecting one value from a list of options is best suited for filter values that cannot be selected simultaneously, helping prevent an empty state.
Numbers, dates, times, and datetimes
By combining an operator (greater than, less than, before, etc.) with input fields, filtering by numerical values, dates, times, and datetimes can be handled. This filtering method is best suited for range-based filtering, i.e., filtering based on comparisons of values or ranges of values.
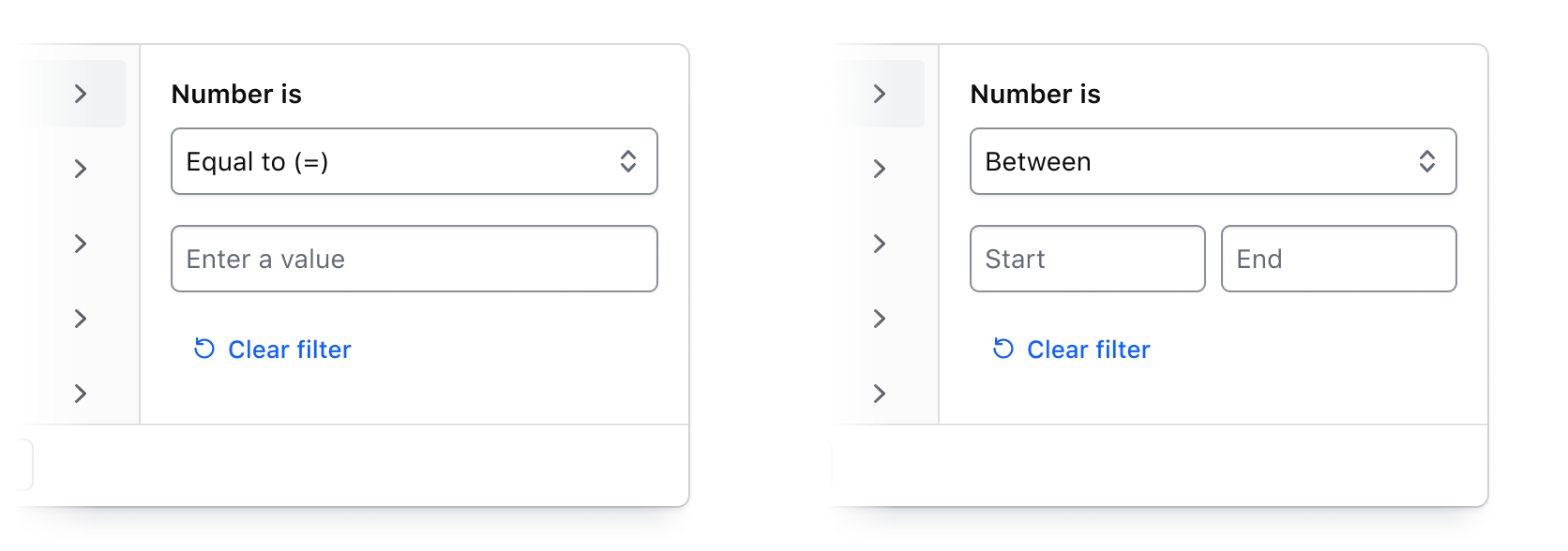
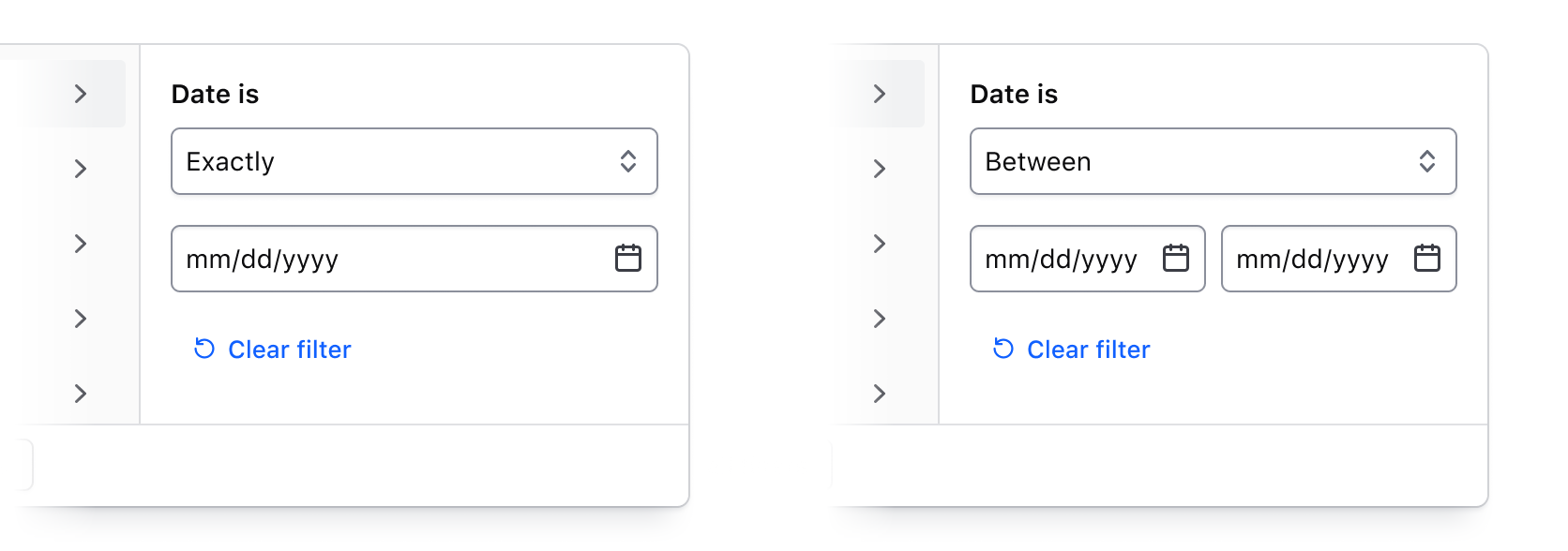
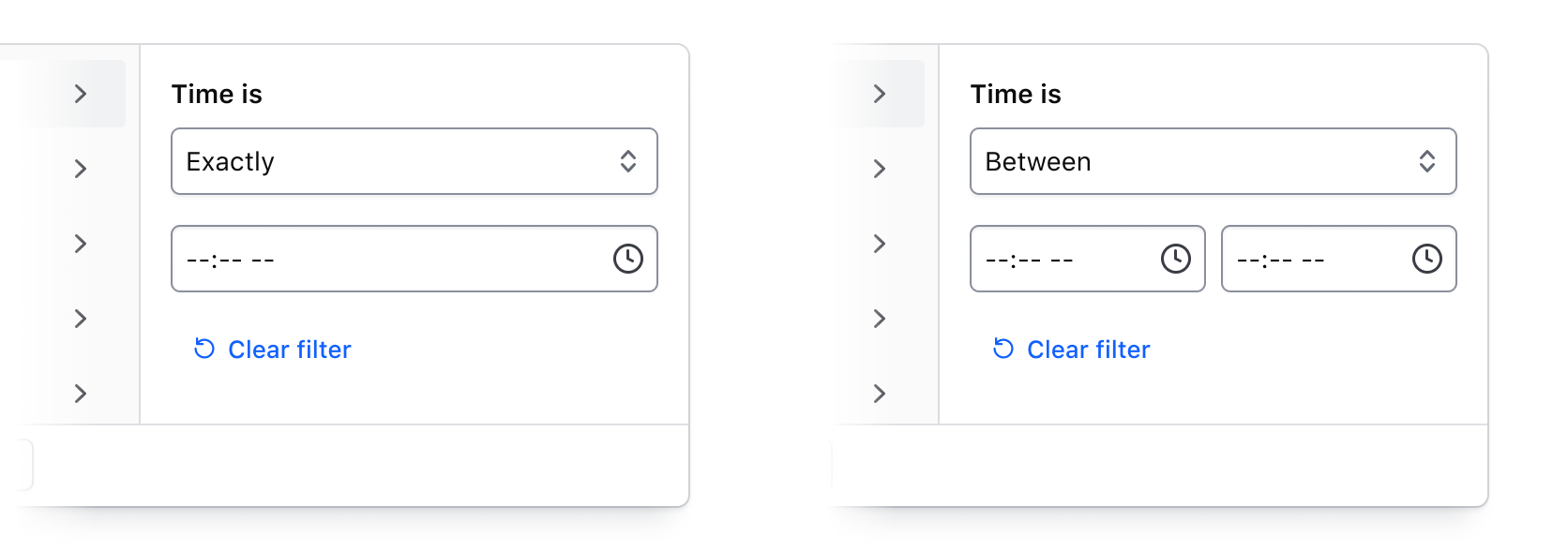
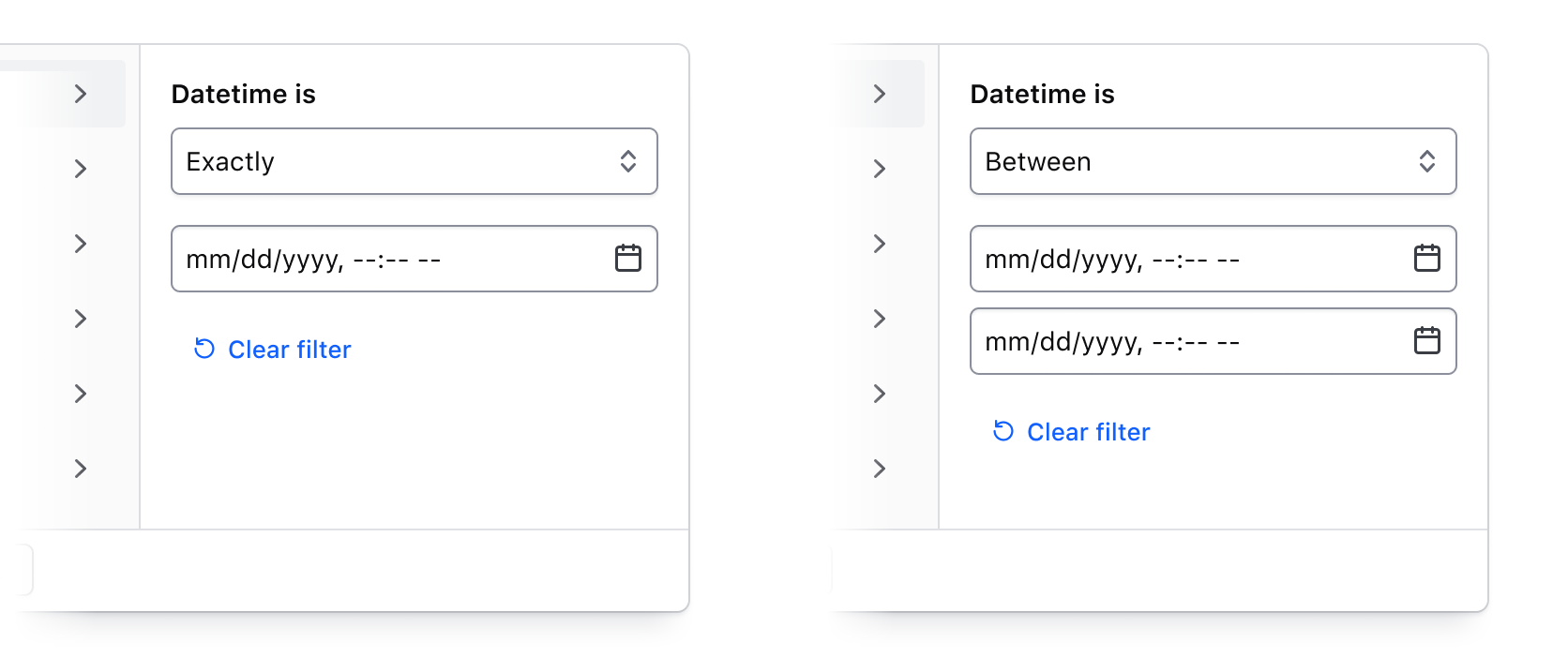
For a full list of supported operators, visit the specifications page.
Custom filtering
While the left panel should always display the list of parameters, the right panel can be customized to meet filtering requirements beyond the out-of-the-box methods.
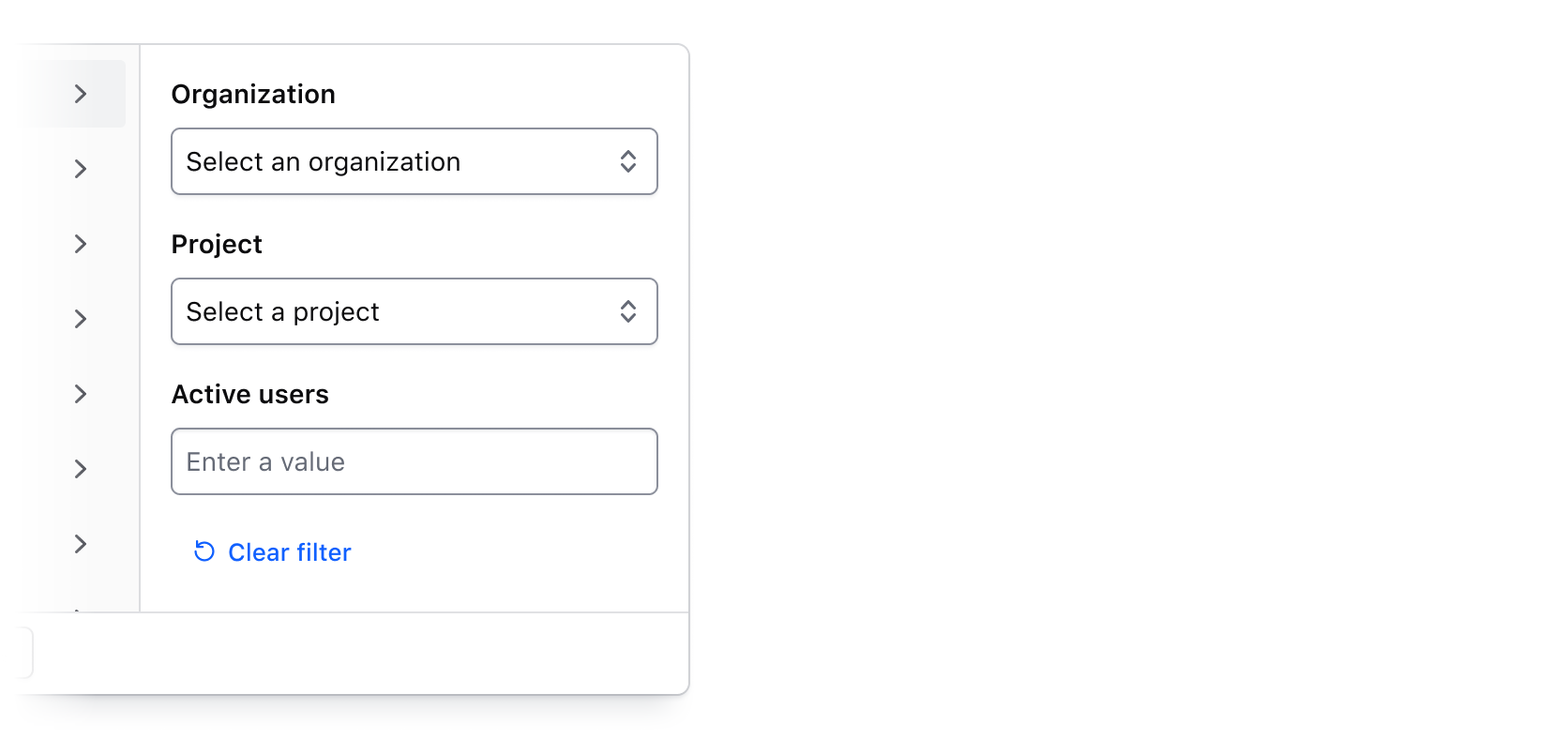
Search across filter values
Users can search across all values within a selected parameter. While search is relevant only for single- or multi-selection, it can be especially useful when there are many values or when a unique naming convention is used.
How to use this component
The Filter Bar component is used to apply and display filters to a data set. The component does not handle any filtering of the data itself, but provides a way for a user to apply filters, and a means for displaying any filters that have been applied.
To use this component, set the filter options available for a data set using the FiltersDropdown and FilterGroup contextual components. When filters are applied, the @onFilter callback provides a data object of the applied filters. To show which filters have been applied, pass a data object of the same structure to the @filters argument.
The Filter Bar is also available as a contextual component of the Advanced Table.